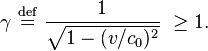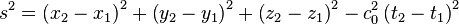Special Relativity
Einstein's theory of special relativity, like Newtonian mechanics, assumes the equivalence of all inertial reference frames, but makes an additional assumption, foreign to Newtonian mechanics, namely, that in free space light always is propagated with the speed of light c0, a defined value independent of its direction of propagation and its frequency, and also independent of the state of motion of the emitting body. This second assumption has been verified experimentally and leads to counter-intuitive deductions including:
- time dilation (moving clocks tick more slowly)
- length contraction (moving objects are shortened in the direction of motion)
- relativity of simultaneity (simultaneous events in one reference frame are not simultaneous in almost all frames moving relative to the first).
These deductions are logical consequences of the stated assumptions, and are general properties of space-time, typically without regard to a consideration of properties pertaining to the structure of individual objects like atoms or stars, nor to the mechanisms of clocks.
These effects are expressed mathematically by the Lorentz transformation
where shifts in origin have been ignored, the relative velocity is assumed to be in the -direction and the Lorentz factor γ is defined by:
The Lorentz transformation is equivalent to the Galilean transformation in the limit c0 → ∞ (a hypothetical case) or v → 0 (low speeds).
Under Lorentz transformations, the time and distance between events may differ among inertial reference frames; however, the Lorentz scalar distance s between two events is the same in all inertial reference frames
From this perspective, the speed of light is only accidentally a property of light, and is rather a property of spacetime, a conversion factor between conventional time units (such as seconds) and length units (such as meters).
Incidentally, because of the limitations on speeds faster than the speed of light, notice that a rotating frame of reference (which is a non-inertial frame, of course) cannot be used out to arbitrary distances because at large radius its components would move faster than the speed of light.
Read more about this topic: Inertial Frame Of Reference
Famous quotes containing the words special and/or relativity:
“People generally will soon understand that writers should be judged, not according to rules and species, which are contrary to nature and art, but according to the immutable principles of the art of composition, and the special laws of their individual temperaments.”
—Victor Hugo (1802–1885)
“By an application of the theory of relativity to the taste of readers, to-day in Germany I am called a German man of science, and in England I am represented as a Swiss Jew. If I come to be regarded as a bête noire the descriptions will be reversed, and I shall become a Swiss Jew for the Germans and a German man of science for the English!”
—Albert Einstein (1879–1955)