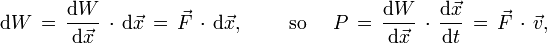Kinematic Integrals
Forces can be used to define a number of physical concepts by integrating with respect to kinematic variables. For example, integrating with respect to time gives the definition of impulse:
which, by Newton's Second Law, must be equivalent to the change in momentum (yielding the Impulse momentum theorem).
Similarly, integrating with respect to position gives a definition for the work done by a force:
which is equivalent to changes in kinetic energy (yielding the work energy theorem).
Power P is the rate of change dW/dt of the work W, as the trajectory is extended by a position change in a time interval dt:
with the velocity.
Read more about this topic: Force
Main Site Subjects
Related Subjects
Related Phrases
Related Words